Simplify your tax filing with our Advanced Income Tax Calculator. Effortlessly estimate your liabilities and discover potential refunds. Try it out today!
User Guide: How to Use the Advanced Income Tax Calculator
Need help with taxes? Use our Advanced Income Tax Calculator for precise calculations and insights. Make tax season stress-free—get started now!
This user guide will help you navigate through the Advanced Income Tax Calculator and understand how to input your financial details for accurate tax calculation.
Steps to Use the Calculator
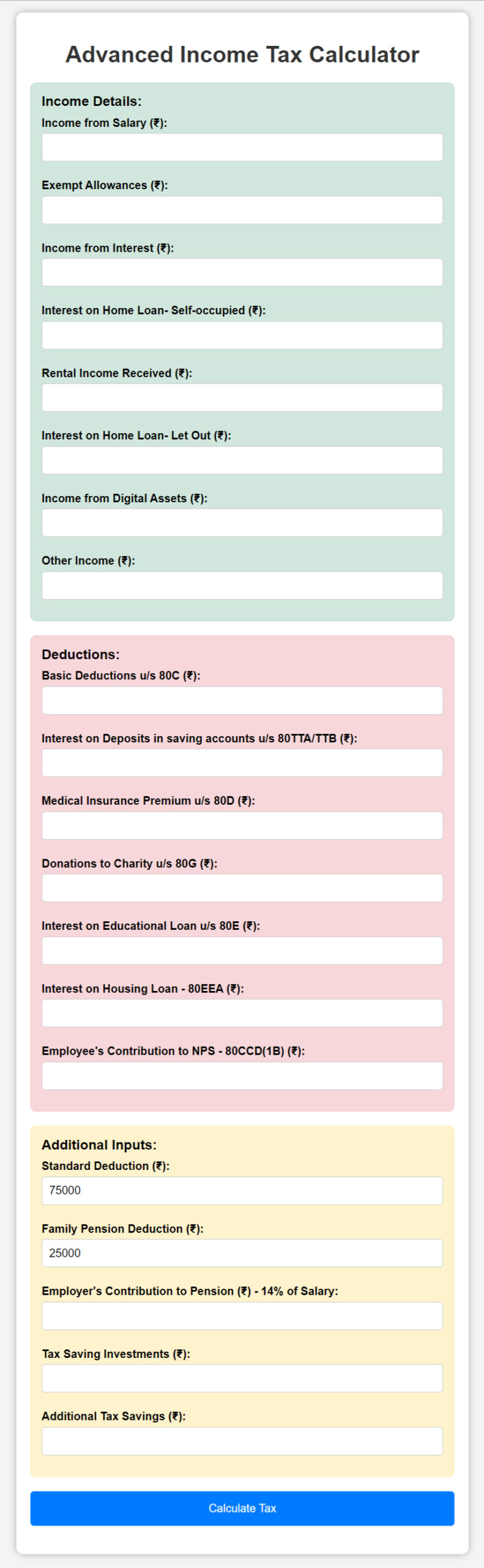
Step 1: Income Details Section
- Income from Salary (₹): Enter your total annual salary before deductions.
- Exempt Allowances (₹): Input any exempt allowances that you receive (e.g., HRA, LTA).
- Income from Interest (₹): Enter the amount of interest you earn from savings or fixed deposits.
- Interest on Home Loan – Self-occupied (₹): If you have a home loan on a self-occupied property, input the interest paid.
- Rental Income Received (₹): If you have rental income from any property, provide the total amount received annually.
- Interest on Home Loan – Let Out (₹): If you have a home loan on a let-out property, enter the interest paid.
- Income from Digital Assets (₹): Enter the income generated from digital assets like cryptocurrencies.
- Other Income (₹): Add any other miscellaneous income you receive during the year.
Step 2: Deductions Section
- Basic Deductions u/s 80C (₹): Enter your total investments eligible for 80C deduction (e.g., PPF, ELSS).
- Interest on Deposits in Saving Accounts u/s 80TTA/TTB (₹): Input the interest earned from savings accounts (for senior citizens, this may include 80TTB deductions).
- Medical Insurance Premium u/s 80D (₹): Enter the total premium paid towards medical insurance for yourself and family.
- Donations to Charity u/s 80G (₹): Enter the amount you donated to charitable organizations eligible for tax deduction.
- Interest on Educational Loan u/s 80E (₹): Provide the interest paid on an educational loan.
- Interest on Housing Loan u/s 80EEA (₹): If you qualify under section 80EEA for a housing loan, enter the amount.
- Employee’s Contribution to NPS u/s 80CCD(1B) (₹): Enter your contribution to the National Pension Scheme (up to ₹50,000 under 80CCD(1B)).
Step 3: Additional Inputs Section
- Standard Deduction (₹): A default deduction of ₹75,000 is already filled for you.
- Family Pension Deduction (₹): This is a deduction for family pension income (₹25,000 is default).
- Employer’s Contribution to Pension (₹): Input your employer’s contribution towards your pension (14% of salary is allowed).
- Tax Saving Investments (₹): Input any additional tax-saving investments.
- Additional Tax Savings (₹): Provide any other tax-saving expenses or investments.
Step 4: Calculation
- Once all fields are filled, click the Calculate Tax button to generate your total taxable income and tax payable.
Step 5: Results Section
- After submission, the calculator will display:
- Total Income: Summation of all income sources.
- Total Deductions: Total eligible deductions.
- Taxable Income: Your income after deductions.
- Total Tax Payable: The final tax amount you need to pay based on the provided inputs.
Important Notes
- All fields are mandatory. Ensure to fill them accurately for an accurate calculation.
- The calculator is based on the new tax regime slabs for FY 2024-25.
- The tax calculation takes into account deductions under sections 80C, 80D, 80G, 80E, 80EEA, and 80CCD(1B), among others.
Transform your tax planning with our Advanced Income Tax Calculator. Quickly compute your income tax and explore deductions. Take control of your taxes!

Here are two live examples for using the Advanced Income Tax Calculator:
Example 1
Scenario: Rohit, a salaried individual, has the following details for FY 2024-25
- Income from Salary: ₹12,00,000
- Exempt Allowances: ₹50,000
- Income from Interest: ₹20,000
- Interest on Home Loan (Self-occupied): ₹1,50,000
- Rental Income Received: ₹1,00,000
- Interest on Home Loan (Let out property): ₹1,20,000
- Income from Digital Assets: ₹70,000
- Other Income: ₹30,000
Deductions:
- 80C Deductions: ₹1,50,000
- 80TTA/TTB Deductions: ₹10,000
- Medical Insurance Premium (80D): ₹25,000
- Donations to Charity (80G): ₹20,000
- Interest on Education Loan (80E): ₹50,000
- Interest on Housing Loan (80EEA): ₹30,000
- Employee’s Contribution to NPS (80CCD(1B)): ₹40,000
Additional Inputs:
- Standard Deduction: ₹75,000 (default)
- Family Pension Deduction: ₹25,000 (default)
- Employer’s Contribution to Pension (14% of Salary): ₹1,20,000
- Investments: ₹1,00,000
- Additional Tax Savings: ₹30,000
Steps:
- Input these values in the calculator fields.
- Click “Calculate Tax.”
Results:
- Total Income: ₹14,90,000
- Total Deductions: ₹5,45,000
- Taxable Income: ₹9,45,000
- Total Tax Payable: ₹37,500
Example 2:
Scenario: Priya, a freelance consultant, has the following details for FY 2024-25
- Income from Salary (Consultancy fees): ₹18,00,000
- Exempt Allowances: ₹0 (None)
- Income from Interest: ₹50,000
- Interest on Home Loan (Self-occupied): ₹0 (No home loan)
- Rental Income Received: ₹2,50,000
- Interest on Home Loan (Let out property): ₹2,00,000
- Income from Digital Assets: ₹1,50,000
- Other Income: ₹1,00,000
Deductions:
- 80C Deductions: ₹1,50,000
- 80TTA/TTB Deductions: ₹10,000
- Medical Insurance Premium (80D): ₹35,000
- Donations to Charity (80G): ₹15,000
- Interest on Education Loan (80E): ₹0 (No education loan)
- Interest on Housing Loan (80EEA): ₹50,000
- Employee’s Contribution to NPS (80CCD(1B)): ₹50,000
Additional Inputs:
- Standard Deduction: ₹75,000 (default)
- Family Pension Deduction: ₹25,000 (default)
- Employer’s Contribution to Pension (14% of Salary): ₹0 (self-employed)
- Investments: ₹75,000
- Additional Tax Savings: ₹0
Steps:
- Input these values in the calculator fields.
- Click “Calculate Tax.”
Results:
- Total Income: ₹23,50,000
- Total Deductions: ₹5,35,000
- Taxable Income: ₹18,15,000
- Total Tax Payable: ₹2,12,500
These examples illustrate how the calculator can be used to compute taxable income and total tax payable based on income and deduction details.
Master your finances with our Advanced Income Tax Calculator. Get real-time calculations and tips to save money. Begin your tax journey now!
Try More Calculators:
Simplify Your Tax Calculation with Our Advanced Income Tax Calculator for FY 2024-25
Are you confused about how much tax you need to pay this financial year? Struggling with the multiple deductions and exemptions that affect your taxable income? Look no further! Our Advanced Income Tax Calculator is here to simplify tax calculations and ensure you make the most of your eligible deductions for the financial year 2024-25.
This intuitive and user-friendly calculator has been specifically designed for Indian taxpayers, keeping in mind the latest income tax slabs under the new regime. Whether you’re a salaried individual, a business professional, or a freelancer, this tool will help you calculate your income tax liability quickly and accurately.
Key Features of the Income Tax Calculator
1. Multi-source Income Calculation
Our calculator accommodates various sources of income, such as:
- Salary
- Exempt allowances (like HRA)
- Interest income
- Home loan interest (for both self-occupied and let-out properties)
- Rental income
- Income from digital assets
- Other sources of income
This feature ensures that no aspect of your income is left out, giving you a comprehensive tax calculation.
2. All Deduction Categories Covered
Our calculator covers all major sections under the Income Tax Act to help reduce your tax burden:
- Section 80C: Investments like PPF, ELSS, LIC premiums (up to ₹1.5 lakh)
- Section 80D: Medical insurance premiums
- Section 80TTA/TTB: Interest on savings accounts
- Section 80G: Donations to charities
- Section 80E: Interest on education loans
- Section 80EEA: Interest on home loans for affordable housing
- Section 80CCD(1B): Contributions to NPS
By including these deductions, our calculator gives you a clearer picture of how much you can save.
3. Automatic Standard and Family Pension Deductions
The calculator automatically considers a Standard Deduction of ₹75,000 and a Family Pension Deduction of ₹25,000. These amounts are included to simplify the process for individuals who are unsure about how to factor these deductions into their taxable income.
4. New Income Tax Slabs for FY 2024-25
We’ve integrated the updated tax slabs under the new tax regime:
- 0% for income up to ₹3,00,000
- 5% for income between ₹3,00,001 and ₹7,00,000
- 10% for income between ₹7,00,001 and ₹10,00,000
- 15% for income between ₹10,00,001 and ₹12,00,000
- 20% for income between ₹12,00,001 and ₹15,00,000
- 30% for income above ₹15,00,000
These rates are automatically applied based on your taxable income, eliminating the need for manual calculations.
5. Comprehensive Tax Breakdown
After entering your income and deductions, the calculator provides a detailed breakdown of your total income, deductions, taxable income, and the total tax payable. This breakdown allows you to review how each section affects your overall tax liability.
How to Use the Income Tax Calculator
Using the calculator is simple and straightforward. Let’s take a look at how you can calculate your taxes using the calculator with real-life examples.
Example 1: Salaried Individual
Meet Rohit, a salaried employee with a gross annual salary of ₹12,00,000. He also earns ₹20,000 from bank interest, has home loan interest of ₹1,50,000, rental income of ₹1,00,000, and ₹70,000 from digital assets. He contributes ₹1,50,000 towards Section 80C (investments) and ₹25,000 towards medical insurance under Section 80D.
Here’s how Rohit calculates his taxes:
- Total Income: ₹12,00,000 (salary) + ₹20,000 (interest) + ₹1,00,000 (rental income) + ₹70,000 (digital assets) = ₹14,90,000
- Total Deductions: ₹1,50,000 (80C) + ₹25,000 (80D) + ₹50,000 (80E) = ₹5,45,000
- Taxable Income: ₹14,90,000 – ₹5,45,000 = ₹9,45,000
- Total Tax Payable: ₹37,500 (based on the new tax regime slabs)
Example 2: Freelance Consultant
Meet Priya, a freelance consultant with a total income of ₹23,50,000, including rental income of ₹2,50,000 and interest from home loan on a let-out property of ₹2,00,000. She invests ₹1,50,000 under 80C and pays ₹35,000 for medical insurance under 80D.
Priya’s tax breakdown:
- Total Income: ₹18,00,000 (consultancy fees) + ₹50,000 (interest income) + ₹2,50,000 (rental income) + ₹1,50,000 (digital assets) + ₹1,00,000 (other income) = ₹23,50,000
- Total Deductions: ₹1,50,000 (80C) + ₹10,000 (80TTA) + ₹35,000 (80D) = ₹5,35,000
- Taxable Income: ₹23,50,000 – ₹5,35,000 = ₹18,15,000
- Total Tax Payable: ₹2,12,500
Why Use Our Income Tax Calculator?
The complexity of modern-day tax calculations can be overwhelming, especially when you have multiple sources of income and several deductions to consider. Our Advanced Income Tax Calculator not only helps you make accurate calculations but also ensures that you don’t miss out on any potential savings.
Here’s why you should choose our tool:
- User-friendly: No need to be a tax expert to use this calculator.
- Comprehensive: Covers all forms of income and deductions.
- Instant Results: Get a detailed breakdown of your taxes in seconds.
- Updated Tax Slabs: Accurate calculations based on the latest income tax laws.
Don’t let the fear of taxes bog you down. With our Advanced Income Tax Calculator, calculating your tax liability is easier than ever. Just input your details, claim the deductions you’re eligible for, and get your tax calculation done instantly.
Take control of your finances today and avoid any last-minute tax surprises!
Calculate your taxes now and save more with the right planning!
How the New Tax Regime Affects Your Income
With the introduction of the new tax regime, taxpayers now have the option to choose between the old tax regime (with deductions and exemptions) and the new tax regime (with lower tax rates but fewer deductions). Let’s break down how the new tax regime can impact your tax liability:
- No Deductions, Lower Tax Rates: Under the new tax regime, popular deductions like Section 80C, 80D, HRA, and standard deduction are not available. However, the tax rates are significantly lower, which could benefit individuals with fewer deductions and exemptions.
- Simplified Tax Structure: The new regime simplifies the calculation process by reducing the need for maintaining investment proofs and records for claiming deductions. It’s a good option for taxpayers who do not heavily invest in tax-saving instruments like PPF, insurance, or NPS.
Our Income Tax Calculator automatically calculates your tax under the new regime, so you can easily compare it with the old regime and choose the one that’s most beneficial for you.
Tax Planning Tips for Maximum Savings
Tax planning is not just about calculating your tax liabilities but also about smart investment and expense management to minimize your taxable income. Here are a few tips to help you make the most of your tax-saving opportunities:
- Maximize Deductions Under Section 80C: Invest up to ₹1.5 lakh in tax-saving schemes like PPF, ELSS, NPS, or life insurance to reduce your taxable income under Section 80C. It’s one of the most popular sections used for tax savings.
- Opt for Health Insurance: Under Section 80D, you can claim a deduction of up to ₹25,000 on health insurance premiums for yourself and your family. If you’re insuring senior citizens, the limit goes up to ₹50,000.
- Consider NPS for Retirement Savings: By investing in the National Pension System (NPS), you can claim an additional deduction of ₹50,000 under Section 80CCD(1B), over and above the ₹1.5 lakh limit under 80C.
- Take Advantage of Home Loan Benefits: If you’re paying interest on a home loan, you can claim a deduction of up to ₹2 lakh under Section 24(b) for a self-occupied property. Additionally, first-time homebuyers can claim an extra deduction under Section 80EEA.
By planning ahead and utilizing the right deductions, you can significantly lower your tax burden. Use our Income Tax Calculator to see how these tips apply to your financial situation, and plan your investments accordingly to achieve maximum savings.
Income Tax: Everything You Need to Know
Income tax is a vital aspect of any financial system, serving as a key source of revenue for the government. It plays a crucial role in funding public services, infrastructure, defense, education, healthcare, and various other essential functions. As a taxpayer, understanding how income tax works and how it impacts your finances is critical for effective financial planning.
In this blog post, we will explore the basics of income tax, how it’s calculated, tax regimes in India, and useful tips to optimize your tax liability.
What is Income Tax?
Income tax is a direct tax imposed by the government on the income earned by individuals, businesses, and other entities. It is calculated based on your annual income, and the tax you owe depends on various factors such as income level, applicable deductions, and exemptions.
In India, income tax is governed by the Income Tax Act, 1961, which classifies taxable income into five heads:
- Income from Salary: Earnings from employment.
- Income from House Property: Income from owning a property, like rental income.
- Income from Capital Gains: Profit from the sale of assets like stocks or property.
- Income from Business or Profession: Profits from self-employment, freelancing, or business activities.
- Income from Other Sources: Earnings such as interest from savings, dividends, or winnings.
Income Tax Slabs for FY 2024-25
Income tax in India is progressive, meaning the rate of taxation increases as your income increases. For individuals, the income tax is charged under two regimes: the Old Tax Regime and the New Tax Regime. Both offer different rates and exemptions.
New Tax Regime (FY 2024-25)
For individuals opting for the new tax regime, the income tax slabs are as follows:
- Income up to ₹3,00,000: 0% (No tax)
- Income from ₹3,00,001 to ₹7,00,000: 5%
- Income from ₹7,00,001 to ₹10,00,000: 10%
- Income from ₹10,00,001 to ₹12,00,000: 15%
- Income from ₹12,00,001 to ₹15,00,000: 20%
- Income above ₹15,00,000: 30%
Old Tax Regime
Under the old tax regime, the rates are similar but allow taxpayers to claim deductions and exemptions like Section 80C, 80D, HRA, and more, which can reduce the taxable income.
How is Income Tax Calculated?
Income tax is calculated based on the total taxable income after accounting for various deductions and exemptions. Here’s a simplified breakdown of how it’s done:
- Determine Gross Income: This includes your salary, rental income, interest from deposits, capital gains, or any other source of income.
- Claim Exemptions: Certain allowances, such as HRA (House Rent Allowance), LTA (Leave Travel Allowance), and others, may be exempt from tax. Ensure you claim these exemptions.
- Deduct Eligible Deductions: You can reduce your taxable income by claiming deductions under various sections of the Income Tax Act. Common deductions include:
- Section 80C: Investments in PPF, ELSS, NPS, LIC premiums, etc. (up to ₹1.5 lakh)
- Section 80D: Health insurance premiums (up to ₹50,000)
- Section 80TTA/TTB: Interest on savings accounts
- Section 80E: Interest on educational loans
- Section 80EEA: First-time homebuyer benefits
- Compute Taxable Income: Once deductions and exemptions are applied, you arrive at your taxable income.
- Apply Tax Rates: Depending on the tax regime you choose, apply the respective tax slab rates.
- Subtract Rebates: The Section 87A rebate allows taxpayers with income up to ₹7,00,000 under the new regime to get a rebate, effectively making their tax liability zero.
- Add Surcharges and Cess: For taxpayers with income exceeding a specific threshold, a surcharge is applicable. Additionally, 4% health and education cess is added to the tax liability.
Differences Between the Old and New Tax Regimes
The most significant difference between the two tax regimes is the availability of deductions and exemptions in the old regime, while the new regime offers lower tax rates but no deductions.
Old Tax Regime
- Offers numerous deductions (e.g., 80C, 80D, HRA, etc.)
- Suitable for those who invest in tax-saving instruments or claim significant exemptions
- Tax rates are higher compared to the new regime
New Tax Regime
- No deductions and exemptions (except for the standard deduction)
- Lower tax rates across income slabs
- Simplified filing process without the need for documentation for deductions
Tax Planning Strategies for Maximizing Savings
- Invest in Tax-Saving Instruments: If you opt for the old regime, maximize your savings by investing in PPF, ELSS, NPS, or 5-year FD to claim deductions under Section 80C.
- Purchase Health Insurance: Under Section 80D, you can claim deductions for premiums paid towards health insurance for yourself, your spouse, and your parents.
- Home Loan Benefits: Claim deductions on the interest paid on a home loan under Section 24(b) and enjoy additional benefits if you’re a first-time homebuyer under Section 80EEA.
- Rebate for Lower Income Groups: Taxpayers earning up to ₹7,00,000 in a financial year can benefit from the rebate under Section 87A and effectively pay zero tax.
Conclusion
Income tax is an essential responsibility for every individual, and understanding how it works can help you plan your finances effectively. Whether you choose the old or new tax regime, it’s important to assess your income, deductions, and exemptions to minimize your tax liability and maximize savings.
By using tools like our Income Tax Calculator, you can easily calculate your tax liabilities, plan for the future, and make informed decisions about your investments. Make sure to file your income tax returns on time and stay updated with the latest tax laws to ensure smooth financial management.
Tax smartly and secure a bright financial future!
Disclaimer
The information provided in this blog post is for general informational purposes only and is not intended as legal, financial, or tax advice. While we strive to ensure the accuracy and completeness of the information, tax laws are subject to change, and individual tax situations can vary. We recommend consulting with a qualified tax professional or financial advisor for personalized advice based on your specific circumstances. The use of any tools, calculators, or strategies mentioned in this post is at your own risk, and we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or results arising from their use.